
Who should take this test and why it’s essential:
This kit is highly recommended for determining elevated thyroid peroxidase (TPO) levels, which can indicate potential autoimmune disorders like Hashimoto’s disease and Graves’ disease. Take proactive steps towards understanding your thyroid condition and optimizing your well-being. Get started with our advanced testing services today.
Advanced Thyroid
Test Kit
Discover the MLD Advanced Thyroid Test:
Capture comprehensive insights into your thyroid function. This advanced kit not only measures thyroid hormone levels in your blood, helping identify hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, but it also detects the presence of thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb). TPOAb serves as a crucial indicator of underlying autoimmune disorders for those with thyroid disease. Take control of your health today and gain a deeper understanding of your thyroid condition with our advanced testing services.


- FSA/HSA Accounts Accepted

Choose How You'd Like To Collect Your Sample
Quickly collect your sample from the comfort of your home using our ground-breaking Quick Draw device or traditional finger prick lancet.

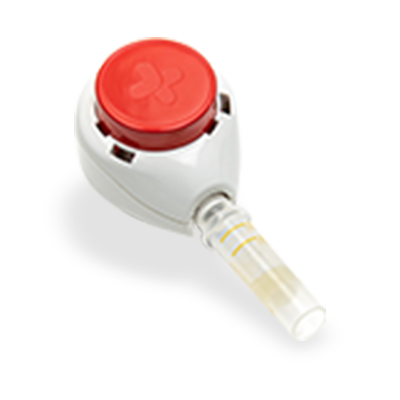
QuickDraw
Collection Method
Description
Our Quick Draw device makes sample collection easy, fast and pain free.
Benefits
- Painless
- Free virtual assistance with collection
- Complete blood results from a single microtainer
- Fast turn-around of results
- Free overnight return shipping
$134.99

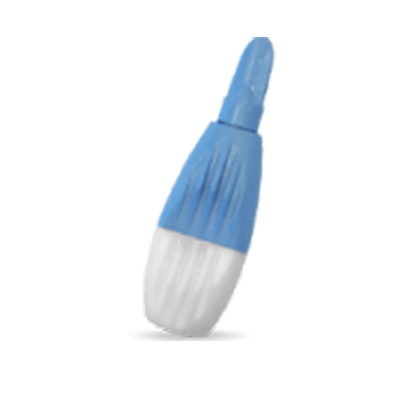
Finger Stick
Collection Method
Description
For those looking for a low cost option, we offer a traditional Finger Stick collection method with a lancet collection device.
Benefits
- Lower cost, although with low to moderate pain
- Complete blood results from a single microtainer
- Fast turn-around of results
- Free overnight return shipping
$104.99
Advanced Thyroid Test Panel
- TSH
- Thyroid Peroxidase Antibody (TPOAb)
- Free T3
- Free T4
Thyroid stimulating hormone is made by the thyroid gland and is released into the blood where it is delivered to tissues in the body. It helps the body stay warm, use energy, and keeps the brain, heart, muscles, and other organs working as they should. TSH can serve as an ‘early warning system’ in the body because it will indicate early changes in thyroid function before thyroid hormones become too high or too low. Because of this, measuring the TSH level in a blood sample is considered the best way to initially test thyroid function.
High TSH levels: The pituitary gland produces more TSH when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. High levels are an indication that the thyroid gland is not making enough thyroid hormone (primary hypothyroidism).
Low TSH levels: Low TSH levels are an indication that the thyroid is producing too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid). Low TSH may result from an abnormality in the pituitary gland. This abnormality prevents it from making enough TSH to stimulate the thyroid.
Symptoms of high TSH levels:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Muscle weakness
- Nervousness or irritability
- Insomnia
- Frequent bowel movements or diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Mood changes
Symptoms of low TSH Levels:
- Weight gain
- Fatigue
- Swelling of face
- Sensitivity to cold temperatures
- Slow heart rate
- Dry skin
- Depression
- Constipation
Thyroid peroxidase is an enzyme found in the thyroid gland. It plays an important role in production of thyroid hormones. A thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPOAb) test detects antibodies against TPO in the blood. If there is a presence of TPO antibodies in your blood, it could be a sign of an autoimmune disorder or may increase the risk of future thyroid disorders.
When the levels are mildly elevated, this can be caused by many thyroid conditions like thyroid cancer, type-1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, as well as auto-immune collagen vascular disease.
High levels of TPO antibodies are usually caused by an autoimmune disease like Hashimoto Thyroiditis, Graves Disease, pernicious anemia, lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. It has been reported that almost 3% of people who have a positive TPO test result do not show any symptoms.
The TPO antibody test is often used to help diagnose Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. The symptoms that may be indicative of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis include:
- Fatigue
- Menstrual irregularities
- Dry skin
- Brittle nails
- Constipation
- Cold intolerance
- Muscles aches and pains
- Depression
- Brain fog
The thyroid produces a hormone called triiodothyronine, known as T3. Most of the T3 in your body binds to protein. The T3 that doesn’t bind to protein is called Free T3. It helps regulate the speed with which the cells/metabolism work. It also regulates your heart rate and how fast your intestines process food. Measuring T3 in the blood is a way to determine if there is a thyroid problem.
High levels of Free T3 levels cause an excessively high metabolic rate and increased risk of hyperthyroidism.
Low levels of Free T3 levels cause slowed metabolic rate and may be a sign of hypothyroidism.
Symptoms of high levels of Free T3 levels:
- Rapid heart rate
- Elevated blood pressure
- Anxiety
- Increased sweating
- Insomnia
- Weight loss
Symptoms of low levels of Free T3 levels:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Puffy face
- Trouble tolerating cold
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Thinning hair
- Depression
- Slowed heart rate
T4, also called thyroxine, is the main form of thyroid hormone made by the thyroid gland. T4 is mostly bound to proteins with a small amount unbound, or free. This test measures the amount of free/or unbound T4 circulating through the blood and indicates how well the thyroid gland is functioning.
High levels of Free T4 may be caused by certain thyroid problems such as thyroiditis, a goiter, high levels of protein in the blood, and hyperthyroidism.
Low levels of Free T4 may be caused by fasting, malnutrition, iodine deficiency, medication that affects protein levels, illness, pituitary problems, and hypothyroidism.
Symptoms of high Free T4:
- Anxiety
- Unplanned weight loss
- Tremors
- Diarrhea
Symptoms of low Free T4:
- Weight gain
- Fatigue
- Hair loss
- Low tolerance for cold temperatures
- Irregular period
- Constipation
How At-Home Testing Works

Step One
Select The Test That's Right For You
Collect your own lab sample anytime, anywhere through an easy-to-use test kit that’s shipped direct to you.
Step Two
Collect And Return Your Sample
Quickly collect your sample from the comfort of your home using our ground-breaking Quick Draw device or traditional finger prick lancet.

Step Three
View YourResults
Your lab results will be available on your personal online dashboard. Results are in an easy-to-understand educational format that helps you manage your health.

We are a REAL LAB,not a marketing company
All tests are processed through our university backed, CLIA certified labs and HIPAA secure results are delivered in real time. After your test is processed, we offer in-depth results to not only help you make important decisions about your health in conjunction with your treating physician or medical team, but solutions to any health issues that may be discovered during the process.
Questions? We Have Answers.
Please prepare to test first thing in the morning. Be sure to drink plenty of water before testing! Being well hydrated will help increase blood flow and improve the testing experience.
*Note: Do not test on a Friday, Saturday, Sunday, or Holiday. Your sample must be picked up, dropped at a dropbox location or brought to FedEx on the same day you test.
Thyroid peroxidase (TPO) is an enzyme normally found in the thyroid gland that plays an important role in the production of thyroid hormones. If you’ve been diagnosed with thyroid disease, a TPO antibody test can be taken to help find the cause. The presence of TPO antibodies in your blood suggests that the cause of thyroid disease is an autoimmune disorder, such as Hashimoto’s disease or Graves’ disease. In autoimmune disorders, your immune system makes antibodies that mistakenly attack normal tissue. TPO antibodies attack the thyroid gland, causing swelling, tenderness and reduced function of the thyroid.
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid stops producing enough T3 and/or T4 and metabolic function becomes impaired. The most common causes of hypothyroidism are autoimmune failure (Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis) and surgical removal or destruction of the thyroid gland which occurs when a goiter is removed or to treat thyroid cancer.
Signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) include:
- Fatigue
- Sleepiness
- Mood swings
- Forgetfulness
- Weight gain
- Depression/irritability
- Muscle cramping and aching
- Weakness
- Decreased perspiration
- Changes in blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Swelling in legs
- Blurred vision
- Cold intolerance
- Hoarse voice
- Heavy menses
- Coarse, dry hair and skin
- Hair loss (on head and/or body)
- Constipation
The thyroid is a small, butterfly shaped endocrine gland located in your neck that produces three hormones: Thyroxine (T4), Triiodothyronine (T3) and Calcitonin. These hormones are secreted into the blood, and two of them, T3 and T4, directly impact your metabolism. How? These hormones regulate how quickly your body’s cells work. If your thyroid secretes too much T4 and T3, your cells will become charged and start working faster than normal – this is called Hyperthyroidism, or overactive thyroid. If your thyroid secretes too little of the hormones, your cells will slow. This condition is called Hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid.
So how does this over or under production of T4/T3 impact your metabolism? T3 and T4 control your heart rate, body temperature and, as it relates to metabolism, they also regulate how quickly your intestines process foods and how fast calories are burned. The condition of under-production of T3 and T4, commonly referred to as Hypothyroidism, can make it impossible to lose weight if not treated. While scientists don’t fully understand why an underactive thyroid causes weight gain or prevents weight loss, they suspect it’s due to:
- Slow Metabolism
- Lack of energy that leads to less activity
- Changes in how your body processes, stores and burns off fat and glucose
- Fluid retention
MLD’s Advanced Thyroid At Home test results will provide detailed information regarding your TSH, free T3, free T4 and TPOAb levels. If your TPO antibodies are positive, and you have a high TSH level, it might mean the cause of your hypothyroidism is an autoimmune disease (e.g. Hashimoto’s disease) and you should consult with a healthcare provider right away.
Comparing TSH with T4 values can provide you and your healthcare provider with a picture of a possible thyroid issue. For example:
- Normal TSH + normal T4 = normal thyroid function
- Low TSH + high T4 = hyperthyroidism/overactive thyroid
- High TSH + low T4 = hypothyroidism/underactive thyroid
- Low TSH + low T4 = low thyroid function due to another problem, such as pituitary gland dysfunction
Your results can be easily shared with your healthcare provider, and in fact, we encourage you to share your data in order to obtain the treatment you might need. Contact us for a network of healthcare providers that specialize in treating hormone deficiencies








