Who should take this test and why it’s essential:
Women who want to gain valuable insights into hormone levels for evaluating infertility, sexual dysfunction, and menopause-related conditions. Take control of your well-being with our comprehensive testing services. Identify imbalances and proactively improve your health. Get started today!
Women's Complete Hormone Test Kit
Discover the MLD Women’s Complete Hormone Test:
Unlock your full potential with optimal female health through the right balance of female hormones. Experience heightened alertness, leaner body mass, and an overall sense of well-being. Discover the power of the MLD Women’s Complete Hormone Health kit, designed to provide essential insights into potential hormonal imbalances by detecting fluctuations in hormone levels. Gain a comprehensive overview of hormone function to identify and address barriers that may be hindering your peak performance. Take charge of your well-being today with our advanced hormone testing kit for women.

- FSA/HSA Accounts Accepted


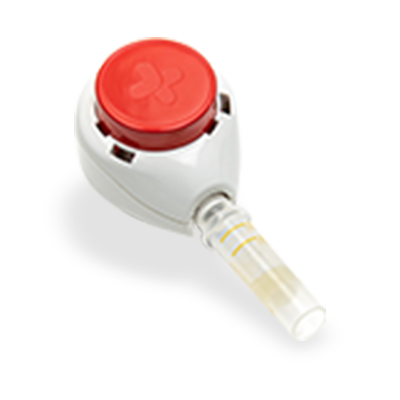
QuickDraw
Collection Method
Description
Our Quick Draw device makes sample collection easy, fast and pain free.
Benefits
- Painless
- Free virtual assistance with collection
- Complete blood results from a single microtainer
- Fast turn-around of results
- Free overnight return shipping
$229.99
What this Test measures
Women's complete Hormone
This test provides you with a complete overview of your hormone health by identifying your hormonal pattern to determine if you are living with too much or too little cortisol, it will allow you to identify hormonal imbalance, and it will allow you to manage your aging process. The hormones within this test are specifically targeted for women.
- Cortisol
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone
- Luteinizing Hormone
- Progesterone
- Estradiol
- Total Testosterone
- Prolactin
Cortisol is produced by the adrenal glands and is the body’s primary stress hormone. It enhances your brain’s use of glucose (sugar) and increases the availability of substances that repair tissues. Its release is increased in response to stress and low blood-glucose levels. It helps regulate metabolism, affects blood pressure, and serves as an anti-inflammatory. Chronically elevated levels of cortisol are an indication a body is stressed which can make healthful eating habits difficult to maintain – the result is often stress-eating which leads to overeating and weight gain.
High cortisol levels – high cortisol levels can be caused by many underlying issues such as overactivity or cancer of the pituitary or adrenal glands, chronic stress and medication side effects. Estrogen can also increase cortisol levels in your blood.
Symptoms of high cortisol:
- Weight gain around midsection and upper back
- Rounding of the face
- Acne
- Slowed healing
- Muscle weakness
- Severe fatigue
Low cortisol levels – low cortisol levels mean the adrenal glands aren’t making enough cortisol. This could be caused by Addison’s disease which could be caused by cancerous cells, removal of the adrenal glands, certain genetic disorders, and certain antifungal medications.
Symptoms of low cortisol:
- Extreme fatigue
- Weight loss
- Dehydration
- Decreased appetite
- Low blood pressure
- Depression
- Irritability
Follicle-stimulating hormone, or FSH, is a hormone that is secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It helps control a woman’s menstrual cycle and egg production. Too much or too little FSH can cause a variety of problems in women.
High levels of FSH in women can be caused by menopause and polycystic ovarian syndrome in which a woman’s hormones are out of balance.
Symptoms of high FSH:
- Irregular period
- Hot flashes
- Disrupted sleep
- Skin and hair changes
- Difficulty getting pregnant
Low levels of FSH are commonly caused by rapid weight loss or being very underweight.
Symptoms of low FSH:
- Irregular or stopped menstrual cycle
- Infertility
Luteinizing hormone, or LH, is produced and released in the anterior pituitary gland. This hormone plays a significant role in controlling the production of estrogen in the ovaries in females. LH plays an important role in sexual development and functioning. Too much or too little LH can cause a variety of problems, including delayed puberty in children, infertility and menstrual difficulties in women.
High levels of LH in women can be caused by menopause and polycystic ovarian syndrome in which a woman’s hormones are out of balance.
Symptoms of high LH:
- Infertility
- Unwanted hair
- Loss of scalp hair
- No period
Low levels of LH in women are commonly caused by recent rapid weight loss, malnutrition, being severely underweight or if the pituitary gland is not working correctly.
Symptoms of low LH:
- Irregular or stopped menstrual periods
- Infertility
- Hot flashes
Progesterone is a female sex hormone that is mainly produced in the ovaries following ovulation each month. It helps regulate the menstrual cycle and maintenance of pregnancy. Without this hormone, a body cannot prepare the right environment for the egg and developing fetus. If pregnant, low levels of progesterone can increase risk of pregnancy loss.
High progesterone levels may mean you are pregnant, have a cyst on your ovaries or a molar pregnancy – an abdominal growth that can cause symptoms of pregnancy.
Symptoms of high progesterone:
- Breast swelling
- Breast tenderness
- Bloating
- Anxiety or agitation
- Fatigue
- Low sex drive
- Weight gain
Low progesterone levels may be caused by menopause, problems with the ovaries or miscarriage.
Symptoms of low progesterone:
- Abnormal uterine bleeding
- Irregular or missed periods
- Spotting and abdominal pain during pregnancy
- Frequent miscarriages
Estradiol is the strongest of the three estrogens in the body and is an important factor in the female reproductive system. In women, estradiol’s main function is to mature and then maintain the reproductive system. Estradiol levels cause the maturation and release of the egg as well as the thickening of the uterus lining to allow a fertilized egg to implant. As women age, levels of this hormone decrease significantly.
Symptoms of high estradiol:
- Acne
- Constipation
- Loss of sex drive
- Depression
- Increased risk of uterine and breast cancer
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease
- Weight gain
- Menstrual problems
Symptoms of low estradiol:
- Absence of menstrual cycle
- Mood swings
- Vaginal dryness
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Osteoporosis
Women produce testosterone in their ovaries and adrenal glands. Testosterone is one of the factors responsible for regulating sex drive, bone mass, fat distribution, muscle mass and production of red blood cells.
High Testosterone: Among women, a high testosterone level may indicate the presence of polycystic ovary syndrome which impacts 6% to 10% of premenopausal women.
Symptoms of high testosterone:
- Acne or oily skin
- Worsened sleep apnea
- Increase in muscle mass
- Excess hair growth on face and body
- Anxiety and Depression
- Deepening of the voice
- Enlarged clitoris
- Infertility
- Thinning of hair
- Loss of libido
- Reduction in size of breasts
- Weight gain
Low Testosterone: Low testosterone levels are called Testosterone Deficiency (TD) or Low Testosterone (Low-T).
Symptoms of low testosterone:
- Fertility problems
- Irregular periods
- Low libido
- Weight gain
- Changes in breast tissue
- Osteoporosis
Prolactin is a hormone that is released from the anterior pituitary gland and is in charge of stimulating milk production, usually after childbirth.
Low Prolactin levels can lead to insufficient milk production after giving birth. Most women with lower prolactin levels don’t usually have specific medical issues, but they may experience a reduced immune response to some infections. Medications could alter levels of prolactin.
High prolactin can cause production of breast milk in women who are not currently pregnant or breastfeeding. High prolactin could be due to a tumor on the pituitary gland, and may also indicate kidney or thyroid disease.
Symptoms of high prolactin:
- Infertility
- Breast leakage in those who are not nursing
- Absent periods
- Low libido
- Painful or uncomfortable intercourse
- Vaginal dryness
- Acne
How At-Home Testing Works

Step One
Select The Test That's Right For You
Collect your own lab sample anytime, anywhere through an easy-to-use test kit that’s shipped direct to you.
Step Two
Collect And Return Your Sample
Quickly collect your sample from the comfort of your home using our ground-breaking Quick Draw device or traditional finger prick lancet.

Step Three
View YourResults
Your lab results will be available on your personal online dashboard. Results are in an easy-to-understand educational format that helps you manage your health.

We are a REAL LAB,not a marketing company
All tests are processed through our university backed, CLIA certified labs and HIPAA secure results are delivered in real time. After your test is processed, we offer in-depth results to not only help you make important decisions about your health in conjunction with your treating physician or medical team, but solutions to any health issues that may be discovered during the process.
Questions? We Have Answers.
In general, women will experience hormonal imbalance at naturally occurring periods in their lives, such as during puberty, pregnancy, menopause and during menstruation. However, hormonal imbalances can also occur as a result of a medical condition, endocrine malfunction, certain lifestyle habits or environmental conditions. Root causes of hormonal imbalances may include compromised gut health, elevated inflammation, and high stress levels.
- Fatigue/Exhaustion
- Skin changes
- Hair growth
- Irregular periods
- Night sweats
**We recommend that you consult with your healthcare provider regarding your test results and treatment.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common of the female hormone disorders. It causes irregular periods, ovarian cysts, weight gain, and fertility problems. PCOS affects about 1 in 10 women of reproductive age.
- Exercise regularly.
- Maintain a moderate weight.
- Watch your gut health.
- Lower sugar intake.
- Reduce stress.
- Get enough sleep.
- Eat healthy fats.
**We recommend that you consult with your healthcare provider regarding your test results and treatment.
Please prepare to test first thing in the morning. Be sure to drink plenty of water before testing! Being well hydrated will help increase blood flow and improve the testing experience.
*Note: Do not test on a Friday, Saturday, Sunday, or Holiday. Your sample must be picked up, dropped at a dropbox location or brought to FedEx on the same day you test.
Your results can be easily shared with your healthcare provider, and in fact, we encourage you to share your data in order to obtain the treatment you might need. Contact us for a network of healthcare providers that specialize in treating hormone deficiencies.














