
Who should take this test and why it’s essential:
Our comprehensive test is highly recommended for individuals with specific health concerns. It is ideal for those with a high protein intake, using performance enhancing drugs, taking medications, managing high blood pressure or diabetes, and dealing with urinary tract issues, kidney stones, or kidney disease. Gain valuable insights into your health and make informed decisions today.
Liver & Kidney Test Kit
Discover the MLD Liver & Kidney Test:
Curious about the health of your liver and kidneys? Our comprehensive test provides insights into their functioning. Whether you’re focused on general health, potential diseases, or monitoring medication side effects, this test offers an overview of your liver and kidney health. Take control of your well-being and gain valuable insights today.


- FSA/HSA Accounts Accepted

Choose How You'd Like To Collect Your Sample
*Receive guidance on using our QuickDraw collection device effectively with a free virtual appointment

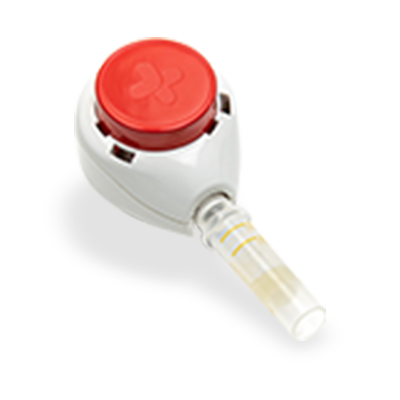
QuickDraw
Collection Method
Description
Our Quick Draw device makes sample collection easy, fast and pain free.
Benefits
- Painless
- Free virtual assistance with collection
- Complete blood results from a single microtainer
- Fast turn-around of results
- Free overnight return shipping
$109.99

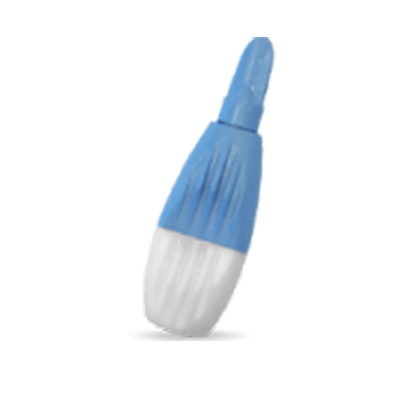
Finger Stick
Collection Method
Description
For those looking for a low cost option, we offer a traditional Finger Stick collection method with a lancet collection device.
Benefits
- Lower cost, although with low to moderate pain
- Complete blood results from a single microtainer
- Fast turn-around of results
- Free overnight return shipping
$79.99
In The DFW Metroplex?
Stop by one of our labs or schedule a mobile concierge to have your sample collected by one of our licensed healthcare professionals.



What this test Measures
Liver & Kidney Panel
Ensuring your liver and kidneys are in good health is vital because these organs help you break down your food and medications, remove waste and toxins, control glucose concentration, fight infections, among other important bodily functions.
- Albumin
- GGT
- BUN
- Creatinine
- Total Protein
- Total Bilirubin
Albumin, one of the most abundant proteins found in the bloodstream, is a protein made by the liver. It helps prevent fluid from exiting the body’s blood vessels. If you have abnormal levels of albumin, it could signal issues with your liver or kidneys or it could signal nutrient deficiency.
High Albumin – Higher than normal levels of albumin might indicate dehydration. Certain medications can cause abnormal levels of albumin.
Low Albumin – Low albumin, or Hypoalbuminemia, can be caused by multiple conditions such as: nephrotic syndrome, malnutrition, heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis. Most cases of low albumin are caused by sudden onset or chronic inflammatory responses.
Symptoms of low albumin:
- Fluid retention
- Appetite changes
- Thinning hair
- Rapid heartbeat
- Weakness or exhaustion
- Vomiting, diarrhea, nausea
GGT, Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase, is an enzyme found throughout the body but most commonly found in the liver. High levels of GGT in the blood could be an indicator of damage to the liver or bile ducts.
Symptoms of abnormal levels of GGT:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Abnormal pain or swelling
- Jaundice
- Weakness or fatigue
BUN, or Blood Urea Nitrogen, is an indicator of liver and kidney function. BUN measures the amount of nitrogen in your blood that comes from the waste product, urea. Urea is the main nitrogenous broken-down product of protein. Urea is made in the liver and leaves your body through urine.
High BUN levels – Can be caused by kidney disease, a high protein diet, an infection or fever, or thyroid issues. It can also be caused by: inflammation, dehydration, stress, GI bleed, poor circulation, or severe burns. If you have high BUN levels, this could be an indicator that you have an underlying health condition.
Low BUN levels -Can be caused by anabolic steroids, higher IGF-1, and/or growth hormone. Genetic deficiency, pregnancy, over hydration, low protein diet, and impaired liver function can also be the cause of a lower BUN value.
Symptoms:
- Frequent urination
- Discolored urine
- Pain
- Fatigue
- Swelling
Creatinine is a chemical compound waste product that comes from the normal deterioration of muscles in the body. Normal levels of creatinine vary based on gender, body size, age, and race. This means there is no “normal” level. Creatinine can indicate how well your kidneys are functioning by how well they are filtering waste from your blood.
High Creatinine levels – Usually indicate there is too much creatine in the body because it is not being removed or filtered appropriately. It could mean that your kidneys are not functioning as they should. A high level of creatinine can be caused from ingesting large amounts of protein or a creatinine supplement. It can also be caused by dehydration.
Low creatinine levels – Could mean lower muscle mass due to aging, liver issues, pregnancy, or a muscular disease. Lower levels found in an older or underweight person should not be a cause for concern.
Symptoms:
- Low muscle mass
- Liver disease
- Faint or dizziness
- Weight loss
Total Protein measures the total amount of two classes of proteins found in the fluid of your blood – albumin and globulin.
High Total Protein levels – If you have high protein levels, this may mean you have an infection such as HIV, blood cancer, or viral hepatitis.
Low Total Protein levels -Having low protein could indicate health conditions such as malnutrition or malabsorption disorders. These conditions could also include liver or kidney disease.
Symptoms:
- Swelling
- Mood changes
- Weakness or fatigue
- Slow healing injuries
- Getting or staying sick
Total Bilirubin refers to all of the bilirubin in your blood including unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin and conjugated (direct) bilirubin.
Low total bilirubin levels – Are nothing to be concerned about as they can be attributed to consuming substances like caffeine or NSAIDS
High total bilirubin levels – Can indicate several health issues such as bile duct problems or liver issues. Less severe conditions such as anemia, reactions to medications, gallstones, Gilbert Syndrome might also cause high levels of total bilirubin.
Symptoms:
- Dark urine
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Weakness and lightheaded
- Chest pain
- Fever
- Chills
- Abdominal pain or swelling
How At-Home Testing Works

Step One
Select The Test That's Right For You
Collect your own lab sample anytime, anywhere through an easy-to-use test kit that’s shipped direct to you.
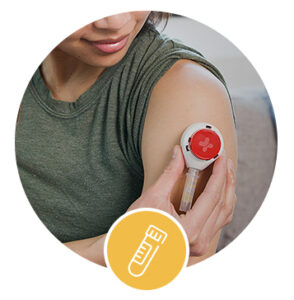
Step Two
Collect And Return Your Sample
Quickly collect your sample from the comfort of your home using our ground-breaking Quick Draw device or traditional finger prick lancet.

Step Three
View YourResults
Your lab results will be available on your personal online dashboard. Results are in an easy-to-understand educational format that helps you manage your health.

We are a REAL LAB,not a marketing company
All tests are processed through our university backed, CLIA certified labs and HIPAA secure results are delivered in real time. After your test is processed, we offer in-depth results to not only help you make important decisions about your health in conjunction with your treating physician or medical team, but solutions to any health issues that may be discovered during the process.
Questions? We Have Answers.
- Abdominal swelling due to fluid due to ascites (a symptom of liver disease)
- Dark-colored urine
- Decreased urine output
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weight gain
- Yellow skin due to jaundice, a symptom of liver disease
- Mental confusion
- Muscle jerks
- Dark leafy green vegetables such as kale, spinach, chard, and collard greens
- Berries
- Cranberries
- Sweet potatoes
- Olive oil
- Fatty fish
- Cabbage
- Oatmeal
- Broccoli
- Coffee
- Green tea
- Almonds
- Spinach
- Blueberries & Cranberries
- Grapefruit
Please prepare to test first thing in the morning. Be sure to drink plenty of water before testing! Being well hydrated will help increase blood flow and improve the testing experience.
*Note: Do not test on a Friday, Saturday, Sunday, or Holiday. Your sample must be picked up, dropped at a dropbox location or brought to FedEx on the same day you test.
Your results can be easily shared with your healthcare provider, and in fact, we encourage you to share your data in order to obtain the treatment you might need. Contact us for a network of healthcare providers in your area.





