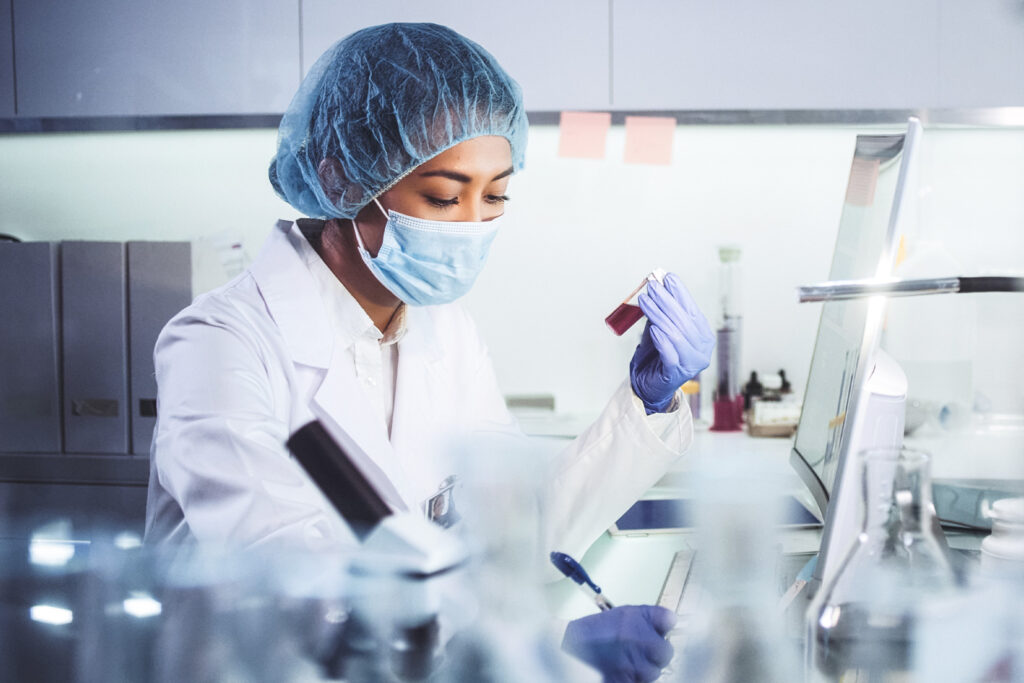
Who should take this test and why it’s essential:
If you’re experiencing persistent lethargy, you may not by properly absorbing nutrients. Vitamins and micronutrients play a vital role in overall health. Routine testing for vitamin deficiencies is essential, allowing you to make informed dietary adjustments or incorporate vitamin supplements into your daily routine. Take charge of your well-being and optimize your nutritional intake today.
Nutrient Health Test Kit
Discover the MLD Nutrient Health Test:
Discover the prevalence of nutrient deficiencies and their impact on your well-being. Feeling sluggish, achy, and not your best? Different nutrient deficiencies exhibit distinct symptoms, making it challenging to pinpoint the specific nutritional gap. Take control of your nutritional health and optimize your well-being by taking our comprehensive Nutrient Health lab test. Identify and address potential deficiencies today for a healthier tomorrow.


- FSA/HSA Accounts Accepted

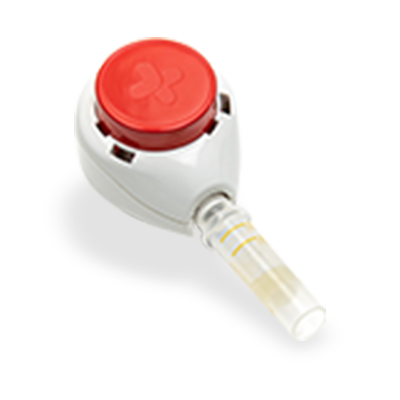
Choose How You'd Like To Collect Your Sample
*Receive guidance on using our QuickDraw collection device effectively with a free virtual appointment

QuickDraw
Collection Method
Description
Our Quick Draw device makes sample collection easy, fast and pain free.
Benefits
- Painless
- Free virtual assistance with collection
- Complete blood results from a single microtainer
- Fast turn-around of results
- Free overnight return shipping
$149.99

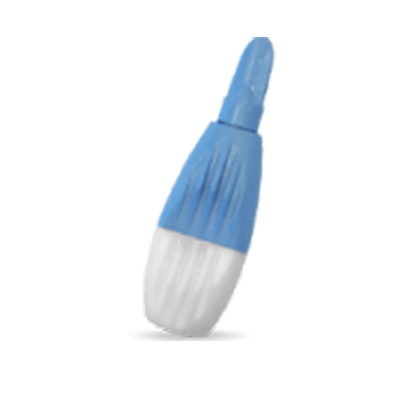
Finger Stick
Collection Method
Description
For those looking for a low cost option, we offer a traditional Finger Stick collection method with a lancet collection device.
Benefits
- Lower cost, although with low to moderate pain
- Complete blood results from a single microtainer
- Fast turn-around of results
- Free overnight return shipping
$119.99
What this test measures?
Nutrient Health Panel
Nutrition testing allows you to evaluate the levels of macronutrients and micronutrients in the blood, giving you better insight into what your body has in excess or if you are experiencing any deficiencies.
Nutritional testing has many uses, such as assessing blood chemistry, hormone function, gut health, metabolic function, blood sugar regulation, food sensitivities and allergies, organ function, and much more.
- Magnesium
- Vitamin B-12
- Folate
- Vitamin D
Magnesium is a mineral stored in your bones, tissues and cells that is important in producing energy, muscle and nerve function, heart health and bone strength. You absorb magnesium into your system through your small intestines when you eat foods such as spinach, whole grains, nuts, beans, bananas, milk, and salmon.
High Magnesium Levels – While not as common as low levels, high magnesium levels are typical in those with kidney damage or those who take certain drugs. Excessive levels of magnesium can cause serious complications, including cardiac arrest
Low Magnesium Levels – Low magnesium levels can indicate inefficient mineral absorption often caused by excessive alcohol consumption, underlying kidney problems, certain medications, celiac disease or chronic digestive issues. Over time, magnesium deficiency can lead to decreased calcium and potassium levels, weak bones and negative effects on your heart.
Symptoms of long-term magnesium deficiency can include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sleepiness
- Headaches
- Weakness and fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle spasms
Vitamin B-12 (cobalamin) is an essential vitamin and plays an important role in blood cell formation, cell metabolism, nerve function and the production of DNA. It is found in foods such as meat, fish, dairy, and fortified foods such as breakfast cereal and is widely available as an oral supplement.
High Vitamin B12 Levels – Abnormally high B12 levels may suggest liver or kidney problems, diabetes, or certain forms of leukemia. Megadoses of the vitamin can lead to acne and rosacea.
Low Vitamin B12 Levels – While vitamin B-12 deficiency is not common in the US, people who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet might be prone to this deficiency because plant foods don’t contain vitamin B-12. Older adults and people with digestive tract conditions that affect absorption of nutrients may also be susceptible to vitamin B-12 deficiency.
Symptoms of low vitamin B12 levels:
- Anemia
- Fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Intestinal problems
- Nerve damage
- Mood disturbances
Folate (vitamin B-9) is important in red blood cell formation for healthy cell growth and function. This nutrient is crucial during early pregnancy to reduce the risk of birth defects of the brain and spine. There is evidence folate can reduce the risk of various cancers and is helpful in treating depression.
High Folate Levels – While excess folate levels aren’t usually dangerous, they are linked to some conditions, including certain types of cancers.
Low Folate Levels – could be caused by the following: high alcohol consumption, diet low in folate, genetic factors and certain medications.
Symptoms of low folate:
- Fatigue
- Gray hair
- Mouth sores
- Tongue swelling
- Growth problems
For most, a balanced diet usually provides all the folate you need. Folate is found in dark green leafy vegetables, beans, peas, nuts, oranges, lemons, bananas, melons, and strawberries. The synthetic form of folate is folic acid and is in many fortified foods, such as cereals and pastas.
Vitamin D plays a major role in regulating your immune system to help you fight off infection. Vitamin D also regulates many other cellular functions in your body. Its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and neuroprotective properties support immune health, muscle function and brain cell activity. Knowing our Vitamin D levels will help you to understand your susceptibility to illnesses.
Low Vitamin D (25-OH D) levels- Deficiencies in Vitamin D can lead to low calcium absorption which in turn causes weakened bones that become soft and brittle and prone to fractures. Perhaps the most commonly known condition attributed to low Vitamin D levels is osteoporosis – a loss of total bone mass. Deficiency in Vitamin D may lead to rickets in children and adverse outcomes in pregnant women and may also contribute to the development of cancer, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
Symptoms of low Vitamin D:
- Fatigue
- Bone pain
- Muscle weakness, muscle aches or muscle cramps
- Mood changes like depression
- Difficulty sleeping
- Hair loss
How At-Home Testing Works

Step One
Select The Test That's Right For You
Collect your own lab sample anytime, anywhere through an easy-to-use test kit that’s shipped direct to you.
Step Two
Collect And Return Your Sample
Quickly collect your sample from the comfort of your home using our ground-breaking Quick Draw device or traditional finger stick lancet.

Step Three
View YourResults
Your lab results will be available on your personal online dashboard. Results are in an easy-to-understand educational format that helps you manage your health.

We are a REAL LAB,not a marketing company
All tests are processed through our university backed, CLIA certified labs and HIPAA secure results are delivered in real time. After your test is processed, we offer in-depth results to not only help you make important decisions about your health in conjunction with your treating physician or medical team, but solutions to any health issues that may be discovered during the process.
Questions? We Have Answers.
Please prepare to test first thing in the morning. Be sure to drink plenty of water before testing! Being well hydrated will help increase blood flow and improve the testing experience.
*Note: Do not test on a Friday, Saturday, Sunday, or Holiday. Your sample must be picked up, dropped at a dropbox location or brought to FedEx on the same day you test.
Iron deficiency occurs when your body does not have an adequate supply of iron. This can be troublesome as iron is used to make hemoglobin, a substance needed to enable red blood cells to carry oxygen. This deficiency is often referred to as anemia and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Extreme fatigue
- Weakness
- Pale skin
- Fast heartbeat or shortness of breath
- Cold hands and feet
- Inflammation or soreness of your tongue
- Brittle nails
- Unusual cravings for non-nutritive substances such as ice, dirt, or starch
To reduce your risk of iron deficiency, you should consume iron rich foods including red meat, pork, seafood, beans, dark green leafy vegetables, dried fruit, peas. In addition to, or in place of iron rich foods, you can also take iron supplements.
When your body is deficient in vitamin D, your bones and muscles take a toll as this vitamin is essential for bone development and maintenance. Vitamin D is needed in order for your body to use calcium and phosphorus to build bones and support healthy tissues. It also plays a role in your nervous system, your musculoskeletal system, and your immune system. Symptoms of vitamin D can look different in children compared to adults:
Symptoms in Children:
Incorrect growth patterns due to bowed or bent bones
Muscle weakness
Bone pain
Deformities in joints
Symptoms in Adults:
Fatigue
Bone pain
Muscle weakness, muscle aches or muscle cramps
Depression or mood changes
There are several ways to curb vitamin D deficiency – most agree the best course of treatment include: sun exposure, taking supplements, and adding foods rich in vitamin D, such as: salmon, tuna, trout, beef liver, mushrooms, egg yolks, and cod liver oil into your diet.
Magnesium deficiencies aren’t commonly discussed, but that may be attributed to the fact that it’s often underdiagnosed. The obvious signs and symptoms don’t appear until your levels are severely low so it’s important that the following are not overlooked:
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shaking
- Muscle spasms
- Hyperexcitability
- Abnormal heart rhythms
This deficiency can be remedied by eating a balanced diet. A magnesium-rich diet consists of leafy green vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Vitamin B12 deficiency is often overlooked as its symptoms are similar to other nutrient insufficiencies but it’s essential for energy production and central nervous system function. The ability to absorb vitamin B12 worsens with age, but children and young adults can also experience vitamin B12 deficiencies. Be on the lookout for the following B12 deficiency symptoms:
- Weakness, tiredness, lightheadedness
- Heart palpitations and shortness of breath
- Pale skin
- Smooth tongue
- Constipation, diarrhea, loss of appetite
- Numbness or tingling, muscle weakness
- Vision loss
- Depression, memory loss, or behavioral changes
Similar to most deficiencies, it can be corrected by eating foods that are rich with that particular vitamin. For vitamin B12, you should add more meat, poultry, seafood, dairy products, and eggs to your diet. You can also add a supplement to your daily routine.
Folate is especially important for women who are pregnant as it aids in the growth and development of unborn babies. Your body needs folate to make new red blood cells and the genetic material in your cells (DNA), hence why it can be troublesome if expectant mothers are experiencing an insufficiency. Regardless of if you are pregnant or not, you should look out for the following symptoms of folate deficiency:
- Extreme fatigue
- Paleness
- Shortness of breath
- Irritability
- Mouth sores or mouth ulcers
- Reduced sense of taste
- Memory loss
- Difficulty concentrating
- Weakness
Eating a well-balanced diet full of leafy greens, citrus fruits, nuts, beans, peas, seafood, eggs, dairy, meat, poultry, and grains can help you prevent folate deficiency. If these foods aren’t a part of your everyday meals, there are also supplements available.
Due to the dietary sources of B12, vegetarians and vegans are at a higher risk of developing vitamin B12 and/or folate deficiencies. You can find folate in peas, beans, citrus fruits, and dark green leafy vegetables whereas vitamin B12 comes from meat, poultry, seafood, and dairy products. Both deficiencies can cause fatigue, weakness, and anemia, however, severe vitamin B12 deficiency can cause complications like depression, paranoia, delusions, memory loss, incontinence and loss of taste and smell.
Your results can be easily shared with your healthcare provider, and in fact, we encourage you to share your data in order to obtain the treatment you might need. Contact us for a network of healthcare providers that specialize in treating nutrient deficiencies.














