
Who should take this test and why it’s essential:
This specialized test is perfect for individuals seeking a deeper understanding of their body’s unique metabolic dynamics. Gain valuable insights into how specific biomarkers influence your metabolism and weight.
Weight Management Test Kit
Discover the Weight Management Test kit:
Uncover the missing link to weight loss with the MLD Weight Management Test kit. Uncover hormonal imbalances impacting your ability to lose weight and stubborn belly fat. Recommended for individuals seeking insights into biomarkers and metabolism.


- FSA/HSA Accounts Accepted

Choose How You'd Like To Collect Your Sample
*Receive guidance on using our QuickDraw collection device effectively with a free virtual appointment

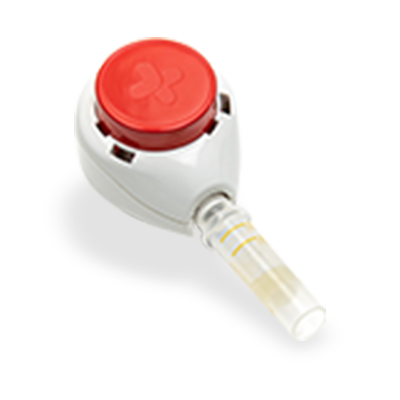
QuickDraw
Collection Method
Description
Our Quick Draw device makes sample collection easy, fast and pain free.
Benefits
- Painless
- Free virtual assistance with collection
- Complete blood results from a single microtainer
- Fast turn-around of results
- Free overnight return shipping
$199.99

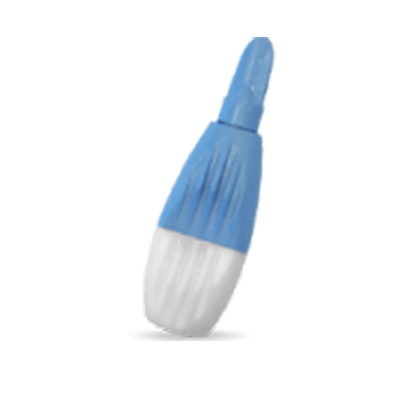
Finger Stick
Collection Method
Description
For those looking for a low cost option, we offer a traditional Finger Stick collection method with a lancet collection device.
Benefits
- Lower cost, although with low to moderate pain
- Complete blood results from a single microtainer
- Fast turn-around of results
- Free overnight return shipping
$169.99
What this Test measures
Weight Management
This test evaluates key biomarkers associated with optimal weight.
- Cortisol
- TSH
- Total Testosterone
- Estradiol
Cortisol is produced by the adrenal glands and is the body’s primary stress hormone. It enhances your brain’s use of glucose (sugar) and increases the availability of substances that repair tissues. Its release is increased in response to stress and low blood-glucose levels. It helps regulate metabolism, affects blood pressure, and serves as an anti-inflammatory. Chronically elevated levels of cortisol are an indication a body is stressed which can make healthful eating habits difficult to maintain – the result is often stress-eating which leads to overeating and weight gain.
High cortisol levels – high cortisol levels can be caused by many underlying issues such as overactivity or cancer of the pituitary or adrenal glands, chronic stress and medication side effects. Estrogen can also increase cortisol levels in your blood.
Symptoms of high cortisol:
- Weight gain around midsection and upper back
- Rounding of the face
- Acne
- Slowed healing
- Muscle weakness
- Severe fatigue
Low cortisol levels – low cortisol levels mean the adrenal glands aren’t making enough cortisol. This could be caused by Addison’s disease which could be caused by cancerous cells, removal of the adrenal glands, certain genetic disorders, and certain antifungal medications.
Symptoms of low cortisol:
- Extreme fatigue
- Weight loss
- Dehydration
- Decreased appetite
- Low blood pressure
- Depression
- Irritability
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) is made by the thyroid gland and is released into the blood where it is delivered to tissues in the body. It helps the body stay warm, use energy, and keeps the brain, heart, muscles, and other organs working as they should. High levels of TSH have been associated with a slow metabolism and weight gain. Measuring TSH levels can help determine if you have underactive or overactive thyroid.
High TSH levels: The pituitary gland produces more TSH when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. High levels are an indication that the thyroid gland is not making enough thyroid hormone (primary hypothyroidism)
Symptoms of high TSH:
- Weight gain
- Fatigue
- Sensitivity to cold temperatures
- Slow heart rate
- Depression
- Constipation
Low TSH levels: Low TSH levels are an indication that the thyroid is producing too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid). Low TSH may result from an abnormality in the pituitary gland. This abnormality prevents it from making enough TSH to stimulate the thyroid.
Symptoms of low TSH levels:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Nervousness or irritability
- Insomnia
- Frequent bowel movements or diarrhea
- Weight loss with increased appetite
Testosterone is a sex hormone that regulates sex drive, muscle mass, bone mass, fat distribution and the production or both red blood cell and sperm in men (in men). It helps male features develop over time and it naturally decreases as men age. The effects of gradually lowering testosterone levels in men are known as late-onset hypogonadism. This condition affects 4 in 10 men by the age of 45. Women also produce testosterone but in much smaller amounts
Low Testosterone: Low testosterone levels is called Testosterone Deficiency (TD) or Low Testosterone (Low-T). This condition is more common in men who are overweight or diabetic. Testosterone usually decreases with age so older men tend to have lower testosterone.
Symptoms of low testosterone in Men:
- Fatigue
- Decreased muscle mass
- Increased fat levels, especially belly fat
- Overall weight gain
- Low libido or sex drive
- Irritability
- Mental fog and memory loss
- Depression and low overall drive
Symptoms of low testosterone in women:
- Increased body fat
- Irritability, depression, anxiety
- Loss of bone density
- Low libido or sex drive
- Vaginal dryness
- Decreased muscle mass
- Thinning hair
- Memory loss
Estradiol is the strongest of the three estrogens in the body and is an important factor in the female reproductive system. In women, estradiol’s main function is to mature and then maintain the reproductive system. Estradiol levels cause the maturation and release of the egg as well as the thickening of the uterus lining to allow a fertilized egg to implant. As women age, levels of this hormone decrease significantly.
Symptoms of high estradiol:
- Acne
- Constipation
- Loss of sex drive
- Depression
- Increased risk of uterine and breast cancer
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease
- Weight gain
- Menstrual problems
Symptoms of low estradiol:
- Absence of menstrual cycle
- Mood swings
- Vaginal dryness
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Osteoporosis
How At-Home Testing Works

Step One
Select The Test That's Right For You
Collect your own lab sample anytime, anywhere through an easy-to-use test kit that’s shipped direct to you.
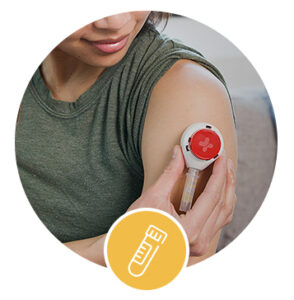
Step Two
Collect And Return Your Sample
Quickly collect your sample from the comfort of your home using our ground-breaking Quick Draw device or traditional finger prick lancet.

Step Three
View YourResults
Your lab results will be available on your personal online dashboard. Results are in an easy-to-understand educational format that helps you manage your health.

We are a REAL LAB,not a marketing company
All tests are processed through our university backed, CLIA certified labs and HIPAA secure results are delivered in real time. After your test is processed, we offer in-depth results to not only help you make important decisions about your health in conjunction with your treating physician or medical team, but solutions to any health issues that may be discovered during the process.
Questions? We Have Answers.
Fat storage and breakdown are strictly regulated by certain hormones in the body. Hormones also influence energy expenditure, or the number of calories your body burns on a daily basis. For this reason, fluctuations in hormone levels may lead to weight gain or loss, as well as body fat accumulation in specific areas.
- You feel less satiated after eating.
- You’re always stressed.
- Your weight gain is only in your abdomen.
- You’re craving sugar.
- You’re hungry all the time.
- You’re losing your hair.
Please prepare to test first thing in the morning. Be sure to drink plenty of water before testing! Being well hydrated will help increase blood flow and improve the testing experience.
*Note: Do not test on a Friday, Saturday, Sunday, or Holiday. Your sample must be picked up, dropped at a dropbox location or brought to FedEx on the same day you test.
Your results can be easily shared with your healthcare provider, and in fact, we encourage you to share your data in order to obtain the treatment you might need. Contact us for a network of healthcare providers that specialize in treating hormone deficiencies.








